The Canadian natural health product (NHP) industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the introduction of new Plain Language Labelling (PLL) Regulations. These updated guidelines, published by Health Canada in 2022, aim to enhance transparency, standardization, and accessibility in NHP labelling. By replacing the previous 2006 regulations, the PLL framework ensures that consumers can easily understand critical product information, including dosage instructions, warnings, and ingredients.
With the increasing reliance on NHPs for wellness and self-care, clear labelling is essential for consumer safety and informed decision-making. Misinterpretation of product labels has been a long-standing concern, leading to accidental misuse or allergic reactions. The updated regulations directly address these risks by mandating standardized formats, enhanced readability features, and bilingual labelling requirements.
Our guide provides an overview of the key regulatory changes, their impact on consumers and industry stakeholders, and the steps businesses must take to ensure compliance with Health Canada’s revised labelling standards
Purpose of Plain Language Labelling (PLL)
The purpose of the Plain Language Labelling Regulations (PLL) is to enhance the accessibility and clarity of health product information for all Canadians. These label requirements are designed to ensure that consumers can easily interpret details such as dosage, potential risks, and ingredients, thereby reducing the risk of misuse or adverse reactions. Under the new requirements, NHP labels must present information in a standardized format using clear, concise language and enhanced readability features.

Standardizing NHP labelling allows consumers to efficiently compare product information across different brands, catering to their needs while ensuring key details are easily accessible. Previously, the 2006 labelling regulations did not require a standardized table format, permitting manufacturers to present information in various ways. While this flexibility benefited marketing and brand identity, it lacked uniformity, requiring consumers to spend additional time reviewing labels to understand a product’s intended use and cautionary statements. The updated regulations address these challenges by introducing a clear and consistent approach to product labelling.
Key Updates to Natural Health Product Labelling Regulations
The new labelling requirements incorporate several substantial changes to enhance clarity and uniformity in labelling practices for natural health products labels, including:
Standardized Product Facts Table (PFT)
The updated regulations for NHPs now require the inclusion of a standardized Product Facts Table (PFT) on product labels to enhance clarity, consistency, and consumer understanding. This table must present essential details such as medicinal ingredients, intended uses, warnings, dosage instructions, storage guidelines, non-medicinal ingredients, and manufacturer contact information.
To ensure uniformity and readability, Health Canada has outlined specific design and formatting requirements, including the use of a sans-serif font with a minimum size, high-contrast colours, and clearly defined borders and line separations. The PFT must also be bilingual, with the option of a single bilingual table or two separate tables for English and French.
While most NHPs must comply with these new standards, certain exemptions apply to products with small packaging, short-term use items, and those with localized effects, such as topical treatments. In cases where label space is insufficient, manufacturers may use fold-out labels, inserts, or direct consumers to online resources.
Mandatory Allergen Labelling

In addition to the PFT requirements, manufacturers must clearly identify common food allergens, including nuts, dairy, wheat, and shellfish, to help consumers with allergies or sensitivities make informed choices and avoid potential adverse reactions. This allergen information must be prominently displayed within the Warnings section of the PFT, ensuring it is easily visible so consumers can quickly recognize any allergens present in the product.
Beyond common allergens, manufacturers must also declare any ingredients sourced from allergenic foods, list gluten sources, and specify added sulphites when present. This expanded labelling requirement aligns with regulations for other consumer products, ensuring greater consistency and transparency in allergen disclosure across different product categories.
Like food labelling regulations, allergens must be declared whenever an ingredient is derived from a known allergenic source. For example, if an NHP contains whey protein, the label must explicitly state “milk” as an allergen, as whey protein is derived from cow’s milk. This requirement enhances consumer safety by preventing individuals from unknowingly consuming allergens that could trigger serious allergic reactions.
Enhanced Readability Standards – Font and Colour Requirements

The labelling update also introduces strict formatting and typographic standards to ensure that labels are clear, readable, and easy for consumers to navigate. All mandatory information must be presented in a non-decorative sans serif font, such as Helvetica or Arial, to maximize legibility. Additionally, all required text must be printed in solid black or a visually equivalent shade, set against a white or nearly white background to create strong contrast. These updates aim to enhance accessibility, ensuring that critical product details are easily understood at a glance.
The regulations also establish specific font size requirements depending on the type of information being displayed. Medicinal ingredients must appear in at least a 6-point font, or 5.5 points if using a condensed typeface. Non-medicinal ingredients must be presented in a minimum 5.5-point font, or 5 points for condensed fonts. These minimum sizes prevent manufacturers from using overly small text that could compromise readability.
To further improve clarity, the rules specify that headings and subheadings within the Product Facts Table (PFT) must be bolded, distinguishing them from the body text, which remains in a regular-weight font. This structured formatting ensures a logical flow of information, making it easier for consumers to locate key details. Additionally, the use of graphics is restricted, except for trademark symbols, Health Canada-approved icons, or other regulatory requirements. This eliminates unnecessary visual clutter and keeps the focus on essential product information.
Bilingual Labelling Requirements
Although not exclusive to the new NHP Labelling Regulations, all required product information must be provided in both English and French to ensure accessibility for all Canadian consumers. This bilingual labelling requirement aligns with Canada’s official language laws and ensures that individuals across the country can access and understand essential details about the products.
To comply with these regulations, manufacturers and designers have two formatting options when presenting bilingual information.
The first option permits a hybrid Product Facts Table where English and French are integrated into a single table. This approach can be beneficial for products with limited label space as shared information between both languages does not need to be repeated.
The second option allows for two separate tables with one dedicated to English and the other to French. While this method ensures clear separation between the two languages it may require additional space on the packaging making it less suitable for products with smaller labels.
Beyond federal requirements manufacturers must also consider provincial labelling regulations particularly in Quebec where language laws are more stringent. Quebec’s Charter of the French Language mandates that all product related information including instructions warnings and ingredient lists be presented in French as prominently as any other language. While federal regulations do not require elements such as marketing copy brand stories or promotional messaging to be translated Quebec law expands these provisions requiring that all consumer facing information including advertisements slogans and company descriptions be available in both French and English.
Manufacturers should carefully review both federal and provincial guidelines to ensure full compliance and avoid regulatory challenges when distributing NHPs across Canada.
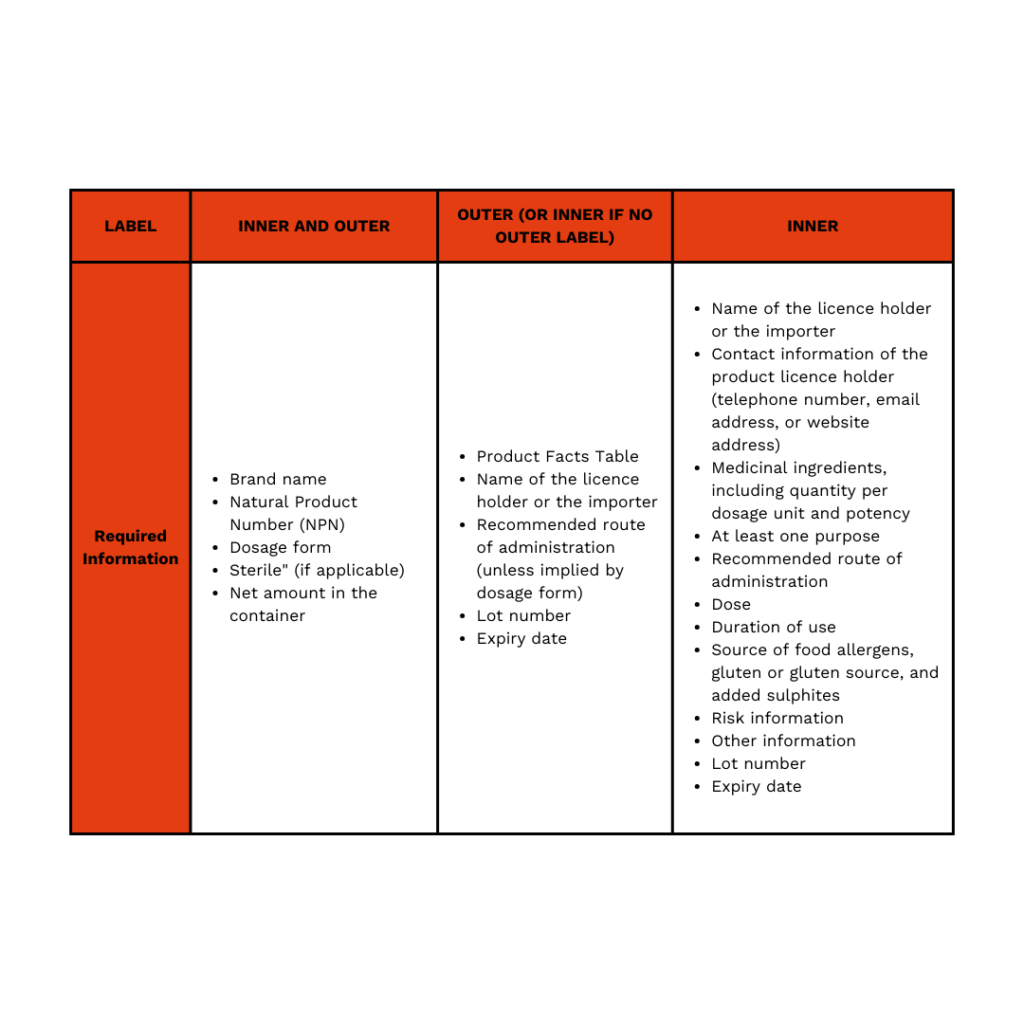
Overview of the Labelling Requirements – Inner vs. Outer Label
For outer labels, or for inner labels when no outer label is used, additional mandatory information must be included. This consists of the Product Facts Table, the name of the licence holder or importer, the recommended route of administration unless it is self-evident based on the dosage form, the lot number for tracking and quality control, and the product’s expiry date.
Inner labels, when a product has both an inner and outer label, have their own set of requirements, ensuring consumers and healthcare professionals have access to all necessary product information. In addition to the name of the licence holder or importer, the label must provide contact information for the product licence holder, which can be a telephone number, email address, or website. The label must also clearly list all medicinal ingredients, including their quantity per dosage unit and potency. At least one intended purpose of the product must be stated, along with the recommended route of administration, the suggested dose, and the duration of use.
Furthermore, any sources of food allergens, gluten or gluten-derived ingredients, and added sulphites must be declared. Risk information, including potential side effects and warnings, must also be prominently displayed. Any other relevant product details must be included, along with the lot number and expiry date, ensuring full traceability and compliance with regulatory standard.
Comparison of Previous and Updated Labelling Requirements
| Feature | Previous Regulations | Updated Regulations |
| Format | Varied among brands | Standardized Product Facts Table |
| Clarity | Often technical and ambiguous | Clear and concise language |
| Allergen Disclosure | Not always provided | Mandatory allergen labelling |
| Readability | No specific font-size requirements, not a structured layout | Requirements for font-size and spacing, structured layout |
| Bilingual Requirements | Mandatory English & French labelling | Mandatory English & French labelling |
Historically, product labels varied significantly in format, structure, and presentation, making it difficult for consumers to quickly locate critical product information. Differences in font sizes, layouts, and terminology between brands often resulted in confusion, requiring consumers to spend additional time searching for essential details such as dosage instructions, warnings, and ingredient lists. This lack of consistency not only complicated decision-making but also increased the risk of misuse, particularly for individuals with limited health literacy or visual impairment.
Additionally, the revised regulations introduce a standardized and user-friendly format that ensures all NHP labels present information in a clear and consistent manner. By mandating uniform formatting across all brands, the updated requirements help consumers quickly and easily identify key details, reducing the time required to find essential product information. The introduction of the Product Facts Table plays a significant role in this improvement by organizing information in a structured and predictable way, mirroring the labelling approach used for non-prescription drugs.
Significance of These Changes for Consumers and Industry Stakeholders
The updated labelling requirements for NHPs mark a significant step in enhancing consumer protection. Many consumers struggle to interpret complex labels, leading to misuse, accidental overdoses, or allergic reactions. By introducing standardized, plain language labelling, Health Canada ensures that essential product information is clear, reducing health risks and improving public safety.

For industry stakeholders, these changes enhance consumer trust, reinforce brand credibility, and help businesses avoid penalties, product recalls, and enforcement actions. Aligning with global labelling standards also strengthens the marketability of Canadian products. Additionally, clearer labels reduce consumer confusion, product misuse, and complaints. While adapting to these updates requires investment in redesign and training, businesses that comply will improve customer satisfaction, strengthen their reputation, and ensure long-term success in a competitive market.
Compliance Deadlines for Industry Participants
Health Canada has revised the compliance deadlines for the new labelling regulations for natural health products (NHPs). Under the latest update, all NHPs must fully comply with the Plain Language Labelling guidelines by June 22, 2028.
Guidelines for Achieving Compliance with the Updated Regulations
To ensure adherence to Health Canada’s revised labelling standards, businesses are advised to undertake the following measures:
Review Health Canada’s updated guidelines: Familiarize yourself with the latest regulatory requirements, including the mandatory Product Facts Table (PFT), font specifications, bilingual labelling rules, and allergen disclosure requirements. Ensure your team understands the scope of these changes and their impact on product labels.
Revise product packaging and labels: Update all labels and packaging to meet the new readability, formatting, and allergen disclosure standards. Ensure that essential information, such as active ingredients, dosage, warnings, and expiry dates, follows the standardized format. Labels must use a sans-serif font in a specific size and be printed in a single color equivalent to 100% solid black.
Implement bilingual labelling requirements: Ensure that all required product information is available in both English and French. Manufacturers can choose between a hybrid table that integrates both languages or two separate tables for each language. Businesses operating in Quebec must also comply with provincial regulations, which may require additional translations beyond federal requirements.
Conduct internal compliance audits: Regularly review and assess product labels to verify compliance with the updated Health Canada regulations. Pay close attention to allergen disclosure rules, as labels must clearly indicate common food allergens, gluten sources, and added sulphites in the Warnings section of the PFT.
Train employees on compliance requirements: Provide ongoing training to staff involved in labelling, packaging, and regulatory compliance. Employees should understand the importance of standardized labelling, how to apply the new rules, and how to minimize errors that could lead to enforcement actions.
Consult regulatory experts and industry specialists: Engage regulatory specialists to ensure a smooth transition and avoid costly penalties, product recalls, or restrictions on sales.
While small and medium-sized enterprises may encounter challenges in adapting to these changes due to redesign costs, training expenditures, and production updates, proactive investment in compliance will prevent costly legal and regulatory complications in the long term.
Learn more about NHP regulations in the Natural Health Product Regulations and NPN Licensing in Canada blog post by SNI.
Regulatory Oversight and Enforcement by Health Canada

Health Canada ensures compliance with natural health product regulations through a robust and multifaceted enforcement strategy. This approach integrates various key measures to safeguard public health and maintain regulatory integrity. When formulating a market entry strategy and establishing control checkpoints, it is essential to consider the following critical factors:
1. Routine audits and inspections: Health Canada conducts regular assessments of businesses involved in the manufacturing, packaging, labelling, importing, storing, distributing, selling, and advertising of NHPs. These inspections ensure adherence to the Natural Health Products Regulations (NHPR) and the Food and Drugs Act (FDA).
2. Product evaluation: Systematic reviews of NHP packaging and labelling are performed to verify accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards. This process ensures that labels provide clear, consistent, and legible information to consumers, aligning with established guidelines.
3. Enforcement actions: In cases of non-compliance, Health Canada has the authority to implement various enforcement actions, including:
Licence Suspension or Cancellation: Health Canada can suspend or cancel product and site licences for NHPs that do not comply with regulatory requirements.
Stop-Sale Directives: Issuing orders to halt the sale of non-compliant products.
Product Seizures: Confiscating products that pose health risks or violate regulations.
Voluntary Recalls: Requesting companies to recall products that are found to be non-compliant or hazardous.
Public Advisories: Issuing alerts and advisories to inform the public about safety concerns related to specific NHPs.
4. Educational support and resources: Health Canada provides industry stakeholders with guidance documents, workshops, and other resources to facilitate compliance with regulations. These initiatives aim to promote a clear understanding of regulatory requirements and support businesses in achieving compliance.
Final Remarks
The introduction of the Plain Language Labelling (PLL) regulations represents a significant step toward improving consumer safety and ensuring clarity in natural health product labelling across Canada. By mandating a standardized Product Facts Table, requiring clear allergen disclosures, and enforcing strict readability standards, Health Canada has taken proactive measures to reduce confusion and enhance transparency in the NHP sector.
For consumers, these changes mean greater confidence in understanding product details, reducing the risk of misuse or adverse reactions. For industry stakeholders, compliance with these regulations not only ensures adherence to legal requirements but also fosters consumer trust, enhances brand credibility, and aligns Canadian NHP labelling standards with global best practices.
While adapting to these new requirements may pose challenges for some businesses, the long-term benefits of improved safety, regulatory clarity, and consumer satisfaction outweigh the initial investment in compliance. As the June 22, 2028, deadline approaches, industry participants must take proactive steps to update their labels, train their teams, and implement best practices to meet the new standards.

Looking to launch your Natural Health Product (NHP) in Canada? Our expert Regulatory Affairs Team at SNI is here to simplify the licensing process from start to finish. Whether you need a straightforward product licence or plan to conduct a clinical trial to support your health claims, we provide the guidance and expertise you need to succeed.
💊 More about our services here.
💡 Compliance is easy with the right support!
📩 info@sourcenutra.com
⬇️ Send us a request for support or an introductory call
FAQ
What is Plain Language Labelling for Natural Health Products?
Plain Language Labelling, or PLL, refers to Health Canada’s updated requirements for how information appears on Natural Health Product (NHP) labels. The goal is to ensure that consumers can easily understand key details like dosage, ingredients, warnings, and contact information by presenting it in a standardized format across all NHPs sold in Canada. All product information must now appear in a standardized Product Facts Table using clear language, readable fonts, strong contrast, and bilingual formatting.
Who needs to comply with the new labelling requirements and by when?
All companies that sell Natural Health Products in Canada must comply with the new regulations. Products licensed before June 21, 2025, must transition to the updated labelling standards by June 22, 2028. Products licensed after June 21, 2025, may temporarily use the older labelling format but will also need to update by the 2028 deadline.
What changes are required for label formatting and design?
Labels must include a bilingual Product Facts Table that clearly outlines the product’s medicinal and non-medicinal ingredients, recommended use, dosage instructions, warnings, storage conditions, and contact details. The label must use a sans-serif font in a minimum size, with high-contrast black text on a white or nearly white background. Headings must be bolded, and sections must be clearly separated to help consumers find information quickly. For more information on labelling specifications and formatting requirements, please visit Health Canada’s NHP labelling regulations.
How must allergens be declared under the new regulations?
Labels must clearly disclose the presence of common allergens such as milk, nuts, wheat, soy, and shellfish, along with gluten sources and added sulphites. All priority food allergen information must be listed in the Warnings section of the Product Facts Table in a way that is easy to find. If an ingredient is derived from an allergenic source, it must be identified accordingly to help consumers avoid potential reactions.
Are there any exceptions to the full labelling requirements?
Yes, certain products may qualify for labelling flexibilities. These include small packages, short-term use items, and products with localized effects, such as topical creams. In these cases, manufacturers may use fold-out labels, inserts, or provide digital access to the full Product Facts Table, as long as the information is available and easy for the consumer to access at the time of use or purchase. For more information on flexibilities, please visit Health Canada’s NHP labelling regulations.