This December 2nd, the SNI Team is celebrating the 5th annual Women’s Brain Health Day. WBHD is an opportunity to recognize that many brain disorders disproportionately affect women, and to advocate for the inclusion of sex and gender in brain research.
This day of awareness was created by Lynn Posluns and her team at Women’s Brain Health Initiative. WBHI continues to work tirelessly to protect the brain health of women, caregivers, and their families while educating women on the ways that they can reduce the effects of cognitive aging.
Almost 70% of Alzheimer’s sufferers are women.
Dementia was previously considered an unpreventable disease that manifested in elderly individuals due to genetics or age, but we are beginning to learn that this is not completely true. Studies have shown that lifestyle choices like diet, physical activity, and stress can drastically impact an individual’s risk of developing dementia. According to WBHI, up to 40% of all cases of dementia may be avoided through lifestyle choices, or an effort to decrease modifiable risk factors. Modifiable risk factors that increase the risk of dementia include smoking, high cholesterol, or high blood pressure.
“We have more control over our cognitive destiny than we may have realized” – Lynn Posluns
What can you do to protect your brain and encourage high cognitive functioning?
The WBHI has identified 6 pillars that cumulatively reduce risk of cognitive impairment and mental decline.
1. Mental Stimulation:
Mental stimulation builds cognitive reserve and neuropathways. This ensures that if one part of the brain falters, another can take over. Although it can be tempting to stick to hobbies or pastimes that you have already mastered, mental stimulation occurs when your brain is actively learning something new. Challenge yourself by learning a new language or skill or take it slow and test your brain by completing tasks with your non-dominate hand. Think of your brain as a muscle; it must be exercised and exerted to maintain its strength!
2. Social Engagement:
Spending time with friends and family is a form of neuroprotection. Social engagement reduces stress and isolation, two known precursors to dementia. Women who have daily contact with friends and family reportedly decrease their risk of dementia by almost half, while women with larger social networks are reportedly 26% less likely to develop dementia than women with smaller social networks. Spending quality time with friends, family, or even pets is an enjoyable way to promote higher cognitive functioning in your future.
3. Physical Exercise:
According to WBHI, individuals who exercise with moderate to rigorous intensity are 36% less likely to be at risk for cognitive impairment and demonstrate increased memory retention over time. Consistent exercise grows the hippocampus, the part of the brain which is involved in learning and memory.
Exercise can combat the age-related shrinkage that the hippocampus is extremely susceptible to. A study completed at McMaster University found that sedentary adults are at the same level of risk of developing dementia as individuals who are genetically disposed to the condition. Daily exercise, like a brisk walk or 10 minutes of aerobic movement, is a great way to encourage better cognitive functioning in your future.

4. Sleep:
The quality and duration of your sleep can have detrimental effects on your brain health. Sleepless nights leave harmful toxins in the brain, known as amyloid plaque. Amyloid plaque deters the retention of new memories and plays a role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Factors like alcohol, cigarettes, caffeinated beverages or foods, noise, or irregular sleep-wake schedules can disturb your sleep. It is recommended that individuals receive 7-8 hours of sleep each night.

5. Healthy Diet and Nutrition:
Your stomach and brain may be more closely connected than you realize, and not just in the case of a flashy food commercial making your stomach growl! Organisms in our stomach, known as gut microbiota, influence our brain and the way that we think. The brain and the stomach link digestion, mood, and health, and brain disorders like Alzheimer’s, depression, and Parkinson’s disease have been linked to altered gut microbiota. Adhering to the MIND Diet is one of the most effective methods of protecting the brain and reducing cognitive decline. The MIND Diet is a combination of the Mediterranean Diet and the DASCH Diet; it protects the brain by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
6. Stress Reduction:
Stress can cause shrinkage in the prefrontal cortex, which may negatively impact an individual’s ability to regulate their emotions, control impulse behaviours, or make decisions. Chronic stress releases cortisol into the body, which can cause premature damage to the brain. Cortisol can shrink, kill, or impede on the generation of neurons in the hippocampus, which can lead to memory loss or the loss of ability to make new lasting memories.
Practicing self-care can reduce stress, so ensure that you are taking time for your own mental health and well-being. Yoga, journalling, and meditation are examples of self-care that can help combat symptoms of stress.
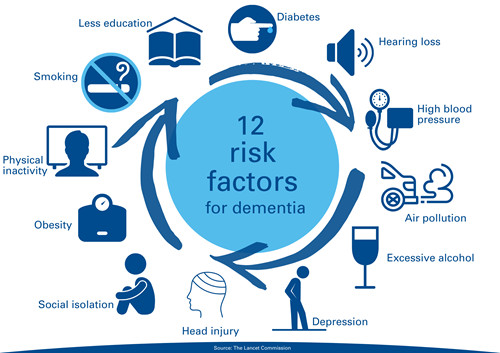
Modifiable Risk Factors that Increase the Risk of Dementia:
According to a study published by The Lancet, there are 12 modifiable risk factors that collectively account for nearly 40% of dementia cases worldwide:
- Less education
- Hypertension
- Hearing impairment
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Depression
- Physical inactivity
- Low social contact
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Traumatic brain injury
- Air pollution
The potential for dementia prevention is high- protect your cognitive health by limiting modifiable risk factors.
Source: Reduce the risk of developing dementia, Alzheimers New Zealand, 2023.
Individuals who engage in two to three healthy lifestyle factors have a 37% lower risk of Alzheimer's disease, compared to individuals who do not engage in any healthy lifestyle factors or only one healthy lifestyle factor.
New research is discovering that symptoms of dementia diseases appear 20-25 years after the cognitive damage has occurred. This data proves that contrary to what was previously believed, dementia is not a disease of old age.
A study of adults in the United States found that high adherence to the MIND diet was associated with a 53% lower risk of Alzheimers, compared to low adherence.
It is vital that brain protection is taught at a young age and practiced over a lifetime to promote high cognitive functioning and decrease cognitive aging in the future. Join SNI in the celebration of Women's Brain Health Day!
Contact us at info@sourcenutra.com for all your industry inquiries.
Reference: https://womensbrainhealth.org/home#mission